Carving a Product Identity
Building a strong product identity is essential for differentiation and user loyalty. This presentation explores the strategic process of carving out a unique product identity.
Introduction to Product Identity
In today’s crowded marketplace, where products and services are increasingly commoditized, a strong product identity becomes the ultimate differentiator. Product identity goes beyond mere branding—it’s the soul of your product, the reason customers choose you over competitors, and the foundation for long-term customer relationships.
“Product identity is not what you say about your product. It’s what your product says about itself through every interaction.”
Components of Identity
A comprehensive product identity framework consists of several interconnected elements that work together to create a cohesive user experience. These components include your product’s personality, values, visual language, tone of voice, and behavioral patterns.
The core components typically include:
- Personality: The human characteristics your product embodies
- Values: The principles that guide your product’s behavior and decisions
- Visual Identity: Colors, typography, and imagery that represent your brand
- Voice & Tone: How your product communicates with users
- Behavioral Patterns: Consistent interaction patterns and micro-interactions
Identity Crisis Recognition
Many products suffer from identity confusion, where different aspects of the product tell conflicting stories to users. This often manifests as inconsistent messaging, mismatched visual elements, or behavioral patterns that don’t align with the intended brand personality.
Signs of identity crisis include:
- Inconsistent visual design across touchpoints
- Conflicting messaging in marketing materials
- User interface elements that don’t match the brand voice
- Features that contradict stated product values
- Customer confusion about what the product actually does
Strategic Positioning
Strategic positioning involves deliberately choosing how your product will be perceived in the minds of customers relative to competitors. This requires deep market analysis, customer research, and a clear understanding of your unique value proposition.
Key positioning strategies include:
- Category Leadership: Being the best in your category
- Niche Dominance: Owning a specific sub-segment of the market
- Innovation Leadership: Being seen as the most forward-thinking option
- Value Leadership: Offering the best price-performance ratio
- Relationship Building: Creating emotional connections with customers
Visual Identity Design
Visual identity is the face of your product identity. It encompasses everything users see when interacting with your product, from the logo and color palette to typography, iconography, and layout patterns.
Essential elements of visual identity include:
- Color Palette: A cohesive set of colors that evoke the right emotions
- Typography: Fonts that reflect your brand personality
- Imagery Style: Consistent photographic and illustrative approaches
- Icon System: A unified set of icons that speak the same visual language
- Layout Patterns: Consistent spacing, alignment, and structural approaches
Communication Strategy
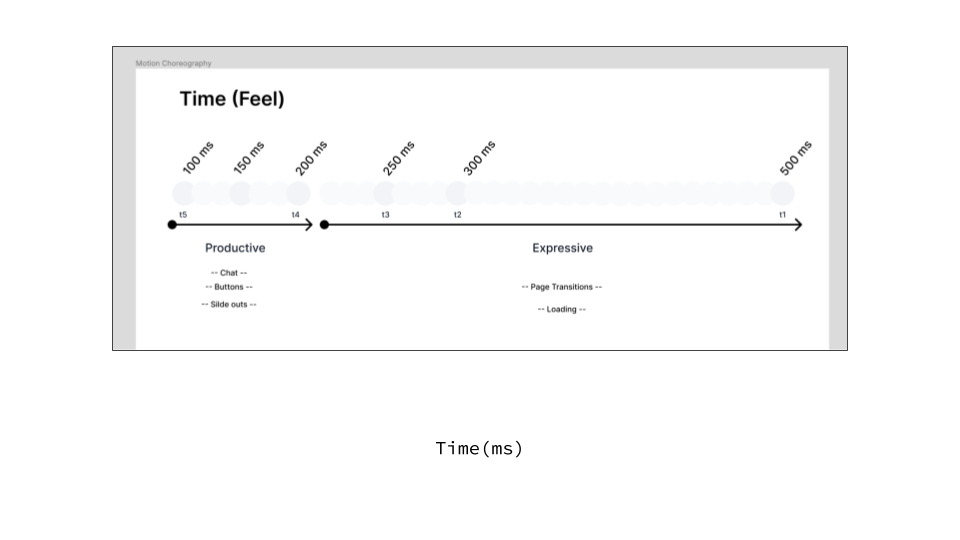
How your product communicates with users is as important as what it communicates. Your communication strategy should be consistent across all touchpoints, from error messages and help text to marketing copy and customer support interactions.
Effective communication strategies include:
- Consistent Voice: Maintaining the same personality across all interactions
- Contextual Messaging: Adapting communication style to different user contexts
- Progressive Disclosure: Revealing information at the right time and pace
- Error Prevention: Designing interfaces that prevent mistakes before they happen
- Helpful Guidance: Providing clear, actionable instructions when needed
Evolution and Adaptation
Product identity is not static—it must evolve as your product grows, your market changes, and customer needs shift. Successful identity evolution requires careful planning, user research, and gradual implementation to avoid alienating existing customers while attracting new ones.
Key considerations for identity evolution:
- Market Changes: Adapting to new competitive landscapes
- User Needs: Responding to changing customer expectations
- Technology Advances: Leveraging new capabilities while maintaining consistency
- Brand Maturity: Evolving from startup energy to established trust
- Global Expansion: Adapting identity for different cultural contexts
Case Studies
Real-world examples provide valuable insights into successful identity transformations. These case studies demonstrate how companies have successfully carved out unique product identities that resonate with their target audiences.
Notable examples include:
- Slack: Transformed from a gaming communication tool to the standard for workplace collaboration
- Instagram: Evolved from a check-in app to the primary platform for visual storytelling
- Airbnb: Built trust and community in an industry known for skepticism
- Spotify: Created emotional connections through personalized music discovery
- Tesla: Established itself as the premium electric vehicle choice through innovation and design
Implementation Roadmap
Implementing a product identity requires a structured approach that balances creativity with practicality. A well-planned roadmap ensures that identity changes are implemented consistently across all touchpoints and user touchpoints.
The implementation process typically includes:
- Discovery Phase: Research and analysis of current state and desired future state
- Strategy Development: Creating the identity framework and guidelines
- Design Phase: Developing visual and interaction design systems
- Implementation: Rolling out changes across products and marketing materials
- Testing and Iteration: Validating identity effectiveness with real users
- Maintenance: Ongoing monitoring and updates as the product evolves
Measuring Success
Measuring the effectiveness of your product identity requires both quantitative and qualitative metrics. Success should be evaluated across multiple dimensions, from user perception to business outcomes.
Key success metrics include:
- Brand Recognition: How well users can identify your product
- User Loyalty: Repeat usage and customer retention rates
- Market Position: Share of voice and mind in your category
- Customer Satisfaction: Net Promoter Scores and user feedback
- Business Impact: Revenue growth, market share, and competitive advantage
- Consistency Scores: How well identity is maintained across touchpoints
Conclusion
Carving a product identity is both an art and a science. It requires deep understanding of your users, clear strategic thinking, and consistent execution across all touchpoints. When done well, a strong product identity creates emotional connections with users, drives business success, and provides a sustainable competitive advantage.
Remember that product identity is not something you create once and forget—it’s a living, breathing aspect of your product that must be nurtured, measured, and evolved over time. The companies that master this art don’t just build products; they build relationships that last.
This post is based on a comprehensive presentation. Full slides and implementation templates available upon request.